|
Side Cover Fan Orientation
Case Airflow
Side Cover Fan Construction
Side Cover Fan Revisions
Cover Fan Cable Assembly
Side Fan Connector
Side Cover Fan Troubleshooting
Deriving 17 V DC from the Power Connector
Part of the following was redone based on info found by Ross Barker.
Contains material from Jim Shorney © 2003 all rights reserved.
Side Cover Fan Orientation
This is a swirling debate... For now, I'd like to point out the difference
between the 95 and 95A plastic end bracket for the fan. The 95A bracket has a
slot and a beefier catch.
From Jim Shorney:
An increasingly common question I'm seeing is "how does that side
fan mount in there?" It seems these fall out easily, and are just as easily
re-installed improperly. The operation of this fan is essential for the health of
the machine, so here are pictures showing proper installation side cooling fan.
This is not documented anywhere in any known IBM
literature, but I would like to thank the kind folks on the
CSIPH newsgroup, and my friends Jason and Mark,
for confirming that this orientation is the correct way to mount the fan for
all 8595 and some 9595 machines. But the picture has still remained unclear,
fostering much debate among PS/2 aficionados.
The first set of photos shown below represent my first attempt to address
this question.
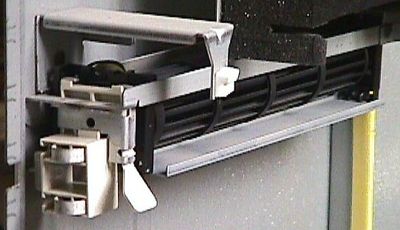
The photo above shows the fan correctly installed on the side
panel of a 9595-0KF.

Here's a closer view of the fan terminals and rear mounting bracket.
To install the fan, you must first orient it properly in the rear support
(the white piece with the electrical contacts). More on this later.
Insert the front mount into the front mounting bracket, and swing the rear
clip with the electrical connections upward into the rear bracket until
it snaps in place. Take care that the wires are routed so they won't
get pinched or crushed, as this could cause smoke!
The electrical contacts don't always make good connection, so it's essential
to verify that the fan actually runs after the side panel is attached to
the computer. If the fan doesn't run, check for dirt or corrosion
on the mating faces of the contacts. Also,
check
the voltage supplied to the fan. The best way that I have found
to make sure the fan is running is to place your ear against the side panel
and power the machine up. You should be able to clearly hear the
fan spin up.
While you've got the fan out, clean the dust from the blades.
It's truly amazing how much a little dust can cut the efficiency of a fan!
9595-xNx, -xPx, -xQx, -xYx, and all 9595A Array Models
After a period of time, and much debate, it began to dawn on me that
there might actually be two correct orientations for the fan. Several
independant sources have indicated that the photos shown above reflect
correct mounting of the fan. However, one person has come to me with
anecdotal evidence that an IBM service rep told him the alternate method
(shown in the photo below) is actually the correct method. He has
also threatened to produce the IBM documentation to support that claim
(more on this as it happens). This mounting would seem to violate
Charles Lasitter's well-reasoned description of
airflow around the CPU complex. After all, why would you blow hot
air on an already hot CPU? But on the other hand, why would you place
another fan to pull against the very strong pull of the power supply fan?
Which is correct?

The most convincing empirical evidence for this alternate mounting is
shown in the next set of photos: the white plastic rear support from a
9595-0PT Type 4 (a.k.a. "95a") has a set of notches in it to accomodate
the flange on the side fan! The fan from a "486xp" case lacks these
notches, which makes it more difficult (but not impossible) to install
the fan with the narrow slot facing the CPU complex. The photo on
the bottom shows a fan from a 9595-0PT. The top photo is of
the fan from a 9595-0KF Type 1 machine.

Conclusion: Both methods are correct!
The first set of photos is correct for the "Model 95xp" case style used
for all 8595, and 9595 non-Type 4 , machines. These
machines have only one serial and one parallel port. (I should note
that these machines can house a Type 4 complex as an upgrade; check the
number of ports on the back to make sure of what you have).
The second set of photos is correct for the so-called "95a" (both array
and non-array) Type 4 machines with two serial and two parallel ports.
There is also a white plastic
air deflector attached to the top of the power supply in some of these
machines, that would seem to angle the airflow from the side fan up towards
the processor complex. The presence of this deflector may have some
bearing on which way the fan is oriented in the 95a box, according to Don
Peter.
But it's not over yet...
Also interesting (although I don't know how relevant) is the slight
difference in shape of the slot immediatly above the fan. I hadn't
noticed this until I had the opportunity to compare "95xp" and "95a" side
panels side-by-side.

Now, on to the great fan debate of '99
(in more-or-less chronological order)
From the godfather Don Peter himself:
I think a lot confusion is caused by misunderstanding
how "tangential fans" (technoslovakian for the squirrel-cage fans) work.
If you look at Jims pictures of the fan you will notice the fan blades
and their angle. The fan rotates "from up to down" corresponding
to the shown orientation. This causes air to be shoveled from the inside
of the "cage" to the outside. On *axial* fans, which have an open cage
to one end it is obvious - the air enters the inside and got pressed out
by the fanblades. But the tangential fan used on the 95 is closed on both
ends (more or less) to hold the axle.
This fan-type takes air from the "lower pressure side" (towards the
top) and presses it through the cage to the "high pressure" side: that
side where the deflector is open - towards the cpu complex.
Terrance fans the fire again:
Peter's explanation just doesn't hold water -" this fan takes air from
the "lower pressure side" (towards the top) and presses it out through
the cage to the "high pressure " side: that side where the air deflector
is open- towards the cpu complex. That is not where the air is blowing
out of my fan. In the position shown in the pictures the air exits the
fan
closest to the side cover blowing down, not at the cpu complex. The
air is entering the fan where you see the blades in the picture, not exiting
from that spot.
"Empirically Louis" Ohland's observations:
OK, propped my side cover up, jumpered the terminals, then "Power On"
(a la CPT Power, good show to watch when drinking rum and coke).
Fact. The fan is installed correctly. How it can be mounted otherwise
makes me cringe contemplating the brute force.
Fact. The majority (if not ALL) fan exhaust DOES go pretty much straight
DOWN. (That hurt, but the hi-tech thread showed the flow)
Fact. The air is being sucked in the top and side of the fan. The thread
was blowing into the blades.... The exhaust is down the side of the side
cover.
Preliminary conclusion- the fan sucks air from the upper part of the
case. The bottom edge of the fan housing mates up (well, close) to the
underside of the complex sucking air away from it.
Confusion. The PS has no vents on the outer side of the system where
the air blows down. The air has to make it's way around the side of the
ps to the front and top of the ps to be exhausted by the ps fan.
My own non-scientific investigation:
I used the cigarette-smoke method on my spare 9595 today. Most
of the airflow into the cabinet seems to be through the upper full-height
drive bay. From there, it is drawn through the power supply and exhausted
out the back.
There doesn't seem to be a lot of airflow into the bottom bay, but there
is
significant airflow through the half-height bay immediately above the FH
bays. This airflow appears to be mainly pulled across the CPU complex
and into the side fan, with some being pulled into the power supply as
well.
This experiment was intended only as a quick and dirty approximation
of airflow around the CPU complex, and is not meant to be a definitive
answer or the final say as to what is actually happening. The addition
of drives or drive blanks to the drive bays will almost certainly result
in more balanced airflow
Charles Lasitter thoughtfully adds:
While I find much of this analysis thoughtful and well considered, I
think this matter of circulation within the case is troubling because of
a paradox that beats scientists with some frequency.
That is, if you remove something from it's environment to study it and
find out how it "really is", then by so doing you kill it and discover
only things that are untrue or misleading.
It's the "fish out of water" syndrome all over again. Want to
study a fish by taking it out of the water and lay it on the
dock? Soon it will be studying a dead fish, and little about
it's nature IN THE WATER will be revealed to you.
The cooling system of the case is a SEALED SYSTEM, operating properly
only when correctly sealed. Beyond being sealed, it is compartmentalized
as well. The compartment seals don't engage until the side access
cover lid is closed!
The compartments and the seals, and how they work in conjunction with
the side louvers tell a great deal of the story.
Look at your side access covers folks! Look at every piece of
steel or foam that's perpendicular to that nice big almost square flat
surface.
Take a close look at how they interlock with the drive support structure
immediately below the FDD's & adapters to keep the hot air from that
area right where it is.
You've got several air movement patterns in this case, and the IBM engineers
spent a lot of time making sure that they didn't work at cross purposes
to one another.
Up at the top of the case, air passes thru the inlet louvers and goes
straight back over and thru the adapters. Why? It has no choice!
Turning downward it's blocked by the flanges from the drive support structure
so that it can't escape around the sides of the "big plastic" and satisfy
the pull from the PSU exhaust.
After making a trip down the length of the adapters, the air moves into
a void between the foam and the side access cover. It moved in here
because this is mostly a low pressure area. Why else would it come
here?
In this area it is exposed to an enormous surface area of the side access
cover fan. It gets pulled thru the fan and exhausted above the PSU,
where the hot air turns a corner to seek out an even larger low pressure
area created by the PSU. The evacuation of the hot air is very slick
at this point, because it comes across one side of the PSU and around the
corner without coming anywhere near (and thereby heating up) the SIMMs
or the HDDs.
Now, for the other major air circulation area.
The drives are cooled in a fairly straightforward way, as air is drawn
directly across the drive surfaces into the waiting vents of the PSU.
But to make sure that TOO MUCH air did not take this route, IBM supplied
each unit with two blank HDD trays, which did a fantastic job of filling
the 2nd HDD bay. This forces inlet air to take a different route.
And what route would that be? Passage thru the top HDD / half-height
bay, which just happens to be -- Ta Daa!! --
immediately opposite that smoking hot CPU.
The airflow runs along the length of the processor board being exposed
along the way and eventually taken up by the side cooling fan and the incredibly
long expanse of louvers on the PSU itself.
If cooling the CPU was your greatest cooling concern, and you weren't
even going to equip that cpu with a CPU fan, why on earth would you blow
how air on it from above that had just come from all those toasty warm
adapters?
Other proof of air movement near the CPU: Which way do the fins
on the CPU point after it's installed on the processor board, and the processor
board is installed on the planar?
If the side cooling fan were blowing down on the CPU, and then that
air were moving across the CPU and out the PSU in a straight path that
way, the fins should orient in the opposite way that they do now.
Other observations: The "slot" next to the side fan. Which
way does the air move thru this slot?
Take a look at the inlet louvers again, and where the slot is relative
to the processor board. Finally, look at the location
of the foam barrier relative to the slot. My best guess is that
air moves UP the back side of the processor board, thus cooling it, into
the low pressure area on the other side of the slot, then being shot across
to the PSU.
The plastic flange dividing upper and lower drive support structure
occurs about the level of the processor board. Some
louvers are immediately adjacent to this area but can't "communicate"
well with the main PSU, exposing them to the pull from the side fan thru
this slot. To intensify this pull, it appears that the engineers
have made this slot as long and wide as possible.
Joe Kovacs enters the fray with an interesting bit of trivia:
At Comdex in Las Vegas a few years ago, an IBM engineer who worked on
PS/2 design told me that cooling and air flows are of major concern in
every design. They design everything for a _reliable life of ten
years.
And it continues...
(Jan 16, 2000)
I hate to bring this up again. I really do. The side fan
(in my newly acquired 9595-0PT) was mounted with the small slot aimed towards
the complex. This machine is actually in pristine condition, and
was BIOS level 01, so I doubt it was fiddled with much. Truth is,
it looks like it could have been a spare. Added to that, fellow auction
hound 'Cigar Steve' tells me that he cornered an IBM service rep recently
who is intimately familiar with model 95's, and he said the proper orientation
is to have the small slot pointed at the complex. Steve claims to
have an IBM hardware manual that pictures this; I will browbeat him until
he brings it over for me to scan. I'm starting to wonder if the orientation
was changed at some point by IBM, and each way is correct for a different
type of complex...
From Peter Wendt, Feb. 5, 2000:
The "fan problem" is not yet fully solved. My own T4 P60 9595 for example
has
the fan orientated in the "old fashioned way" as for the 8595. The
fan
retainer however has the notch, which allows the alternative fan orientation
as well. Recently I disassembled a T4-P66 machine at a customer, which
has
never been taken apart since it was installed in '93: and it has the
fan also
installed in the "old" way. So I really wonder what that notch is for.
Guess
that requires more research before we finally can put down the quest
to an
end.
More from Peter, Nov. 5, 2000
To be precise: all my Type-4 systems I have around here (and all I know
of) have
the sidewall fan installed in the "95XP" orientation.
However: none of these have the
plastic air-baffle installed on top of the power
supply. So my best guess is, that there might be a relation between "95XP
orientation / no air-baffle" vs. "Non-95XP orientation / air-baffle".
The air-baffle came with the 95A "Array" models with the 2 x 3 drive cages
and factory installed CD-ROM. So there might also be a dependency, which
I cannot figure out at that point. (Ed. - non-array '95A' boxes have been
sighted in the US that have the air baffle; I have one, a 9595-0PT).
The orientation on the other hand is of lesser importance as long as
there is a sidewall fan in a Mod. 95 at all. The T4-platforms definitely need
one - the cache chips, the memory controller, the CPU no less and the
"companion chips" on the platform emit a lot heat. From the "smaller"
platforms the Type-3 DX50 platform will positively die without a sidewall
fan. Had that once.
Al Brandt chimes in, Jan. 2, 2002
No one knows for sure which orientation is correct for the side fan. A short
while back I came across a late-model 9595-SOC. I opened the case and low and
behold there was a thin white sticker from IBM on the fan stating that "this
sticker must be visible if the fan is in the correct orientation" (or something
of the sort).
The fan is in the orientation pictured on Jim's page for the 95 XP. The
sticker is on the small strip of metal on the bottom facing forward. It
wouldn't be very visible any other way.
Airflow
The fan serves one purpose in either mounting orientation, that of pulling
air IN through the grilles at the top front of the 95, then THROUGH the
adapters, then DOWN the side wall.
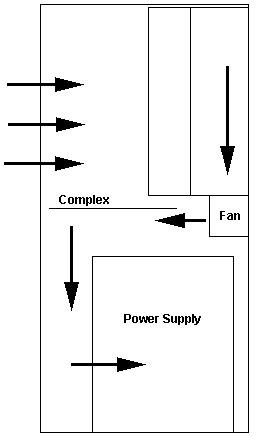
Open to interpretation... The significant points- air is pulled through the
top grilles, sucked through the adapter cards, down the side wall through the
side wall fan.
Air is sucked over the top of the PSU, past the complex, over the memory,
then into the PSU where it is blown out through the exhaust. Though looking at
a PSU shows the memory has a blank surface in front of it, probably to force
airflow past it.
Note: The PSU for the 3511 Enclosure has the
louvers on the lower, inner edge taped off. These louvers ventilate the SIMMs
on the 95 planar. YMMV, I need to source this factoid...
Side Fan Construction
From Peter:
But please do not forget that this thing is not just a simple
"motor". It is an electronically regulated, brushless DC-motor. The electronics
sits under the end facing to the rear - you can see the printboard and some of
the coils. The electronic itself consists out of some resistors and condensers,
ICs, a hall-generator for measuring the rotational speed and so on.
Unlike to "real motors" the resistance does not change when you turn the
fan... normal DC-motors act as generators once driven. This thing doesn't.
However: 137 Ohms would give a current of about 125 mA
- still below the specs.
Side Fan Revisions
64F4470, EC C31557, mfd. 042391, 137 Ω
64F4470, EC C32546, mfd. 121391, 1.31 KΩ
Hosiden HMK 3404-01-092, DC 17 V, 0.185 A
64F4470, EC C32546, mfd. 031892, 1.32 KΩ
Hosiden (flower symbol?) W, HMK 3404-01-092, DC 17 V, 0.185 A
95A Side cooling fan fan
ASM P/N 61G3813, mfd. 101993, 1.32 KΩ
Hosiden (flower symbol?) J, HMK 3404-01-092, DC 17 V, 0.185 A
Possibly this means any fan made on or after 121391
will be a 1.3 KΩ model.
Cover Fan Cable Assembly
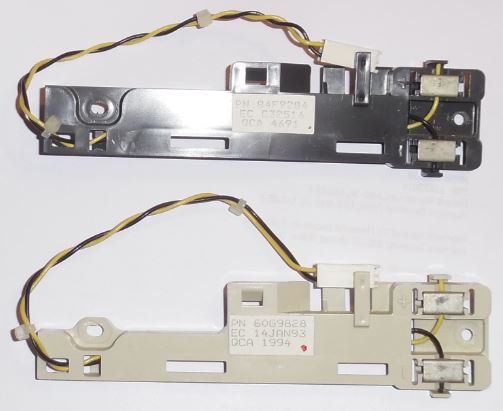
HMM says 61G3824, the older style is P/N 84F9284, the newer style is P/N
60G9828. For purposes of clarity, I wedged the white planar connector into the
top.
The older one is black, and has a full-height pocket for the inner mounting
screw.
The newer one is off-white and the bracket is redesigned to be half as high,
but with a loop sticking up high enough to mate with the mounting post.
Screw appears to be a 3 to 3.5 mm by 8 mm long trilobular screw, double
pitch (like they stretched the screw and the thread is farther apart).

Side Fan Connector
The fan connector is located on the planar and provides 17 V DC directly
from the power supply. It does this by combining the +5 V and -12 V rails.
Pinout of the side fan planar connector (male, top view):
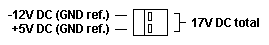
Side Fan Troubleshooting
If the access cover fan does not work:
Check the spring contacts on the fan bracket to see that they
stick out far enough. Over time, with repeated removal and installation of the
side cover, the contacts will be pushed back into their guides. Carefully pull
them out again. Make sure the free end of the spring enters the recess when not
under pressure (that way it's lined up when you are using BOTH hands to install
the side cover...)
Power to fan: 17 V DC (+/- 1.4 V DC) at the two fan cable pins on the
base.
If voltage is correct, check for 1.3 KΩ (+/- 10%) between fan
terminals.
Ed. I have an older fan that has 137 Ω. Runs
fine. See HERE.
If resistance is incorrect, replace the fan. If resistance is correct, check
spring clip connectors. (If good, there isn't a fan problem).
If voltage is incorrect, unplug fan cable from connector J28 on planar and
check cable assembly for continuity. If cable has continuity, replace the
system board (uh, unlikely to be bad). If the cable does not have continuity,
replace it.
Deriving 17 V DC from the power connector
OK, you have a 9595-3Px, fully loaded with RAID drives and memory. BUT you
notice strange erratic performance after a few minutes. After checking, you
notice (to your horror) that you have NO voltage (or not enough) from J28.
Just trot down to Best Buy and pick up the dual serial/parallel planar for
$49.99 and pop it in? Or will you whip out your trusty 25W soldering iron and
take charge of your own destiny? If you are of the adventurous type, read
on!
> That was my intent - how to derive an alternate source of 17 V DC from
the planar power socket...
Pin 7 of the PSU-connector delivers -12 V, pin 3 +5 V... both add to +17 V.
Only need to watch the polarity. (Ed. Verify the
polarity with a voltmeter/DMM. Do not assume anything with a 9595 dual
serial/parallel planar. One bzzt! and you may burn something else on the
planar. The Power Supply will be fine though...)
Tom adds:
The side fan circuit on the planar is unlikely to fail, as it
consists of two direct connections from the main power connector to the fan
header. So if you don't measure 17 V DC there, one of the voltages that are
used to generate it (+5 V and -12 V) is probably missing. (Note: I have removed
the section about the alternative method that used the non-existent -5 V power
rail.)
|