|
@8EFC.ADF IBM PS/2 Fast/Wide SCSI Adapter (Uses same ADF as SE F/W)
C8EFC.ADF Init file for @8EFC.ADF
194-145 IBM SCSI-2 Fast/Wide Adapter/A, SCSI-2 Differential Fast/Wide Adapter/A (PS/2)
ZG94-0165 IBM SCSI-2 Fast/Wide Adapter/A, IBM SCSI-2 Differential Fast/Wide Adapter/A (RS/6000)
rev71upd.exe SCSI-2 Fast/Wide Adapter Firmware Upgrade .71
corv77.exe SCSI-2 Fast/Wide Adapter Firmware Upgrade .77
corvC9.exe SCSI-2 F/W Enhanced Fast/Wide Firmware Upgrade FRU 93H7896 & 52G3380
ibm2.exe F/W and OS/2 2.1 Fix '94 (ibm2scsi.add and ibm2m57.add)
scsi2fw.exe SCSI-2 F/W Support Diskette v2.0
scsi2fw.txt Readme for scsi2fw.exe
SCSIFIX.ZIP A utility to alter the number of
sectors for a SCSI drive and convert them to a 3.94GB drive. (thx Bob Eager!)
SPOCK206 IBM SCSI Driver for Windows 95/98 and Windows NT by Unal Z
Possible MCA Interface Chip Problems
Differential SCSI-2 Fast/Wide Adapter
Rework on 11H7660 Front
Rework on 11H7660 Back
Enhanced Differential SCSI Fast/Wide Adapter
Rear of Enhanced DFW
Jumpers on the Fast/Wide
Further Info
Differential SCSI Fast/Wide Adapter "Corvette Turbo"
FRU P/N 11H3599 (no workee) / 11H7660 (workee) (RS/6000 4-6)
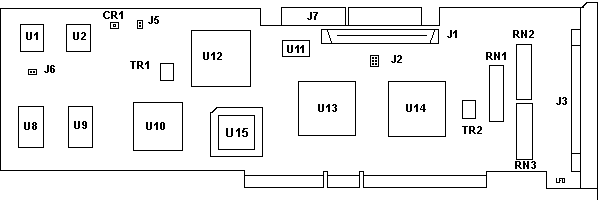
CR1 LED
J1 50-pin SE SCSI connector
J2 2x3-pin diagnostic header
J3 C68 DFW SCSI connector
J5 Leave open. Not used.
J6 Boot Enable
J7 FW SE SCSI connector
RN1-3 RS6K only?
TR1 PTC resistor for internal bus
TR2 PTC resistor for external bus
|
U1 SCSI microcode 61G3929
U2 SCSI microcode 61G3930
U8,9 CXK581000AM-70LL 128Kx8 SRAM
U10 AMD N80C186-20 MCU
U11 40.0000 MHz osc
U12 82G2645 Int. SE SCSI ctrl. "Cutlass"
U13 61G2323 MCA Bus iface "Malibu"
U14 52G9707 Ext. Diff SCSI ctrl. "Cutlass?"
U15 PLCC ROM socket (empty)
|
RN1-3 Removed on RS/6000 systems when a
high-reliability configuration is used (one of them there "Y" arrangements
illegal to normal SCSI users).
Yellow Termpacks
Differential SCSI uses a standard passive resistor termination. This terminator
remains unchanged from the original SCSI-1 standard to the proposed SCSI-3
physical layer. So you might be confused why a newer SCSI adapter uses the
older yellow termpacks like the three can Spock.
The SCSI-2 Differential Fast/Wide Adapter/A supports an internal
single-ended and an external differential SCSI bus.
FRU 11H3599
To date, all attempts to get this RS/6000 adapter to work in a
PS/2 have failed. Although the chipset is the same as on the Fast/Wide, the rev
.71 flash update does not recognize a F/W chipset.
FRU 11H7600
This FRU with a PLCC socket WILL work with no special poodle
faking. User "No Deal" has posted images of the Set Configuration and Set and
View SCSI Devices screens.
Fast/Wide in 8590/8585
If you don't have a Type 4 complex on a 95A (dual serial/dual
parallel), you may not be able to use some features of the Fast/Wide, most
notably Internal/External Bus Mode. You need to run
SCSI2FW.EXE to update the system partition.
FRU 11H7660
To my surprise, the 11H7660 configures fine, flashes to .71, and
works like a normal F/W.
Front 11H7660 DFW Rework
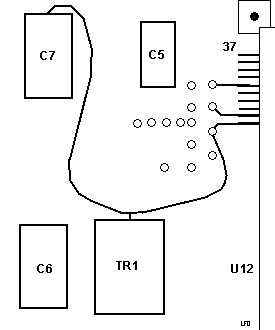
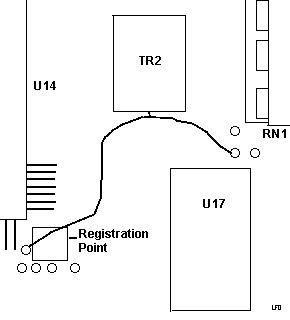
Rear 11H7660 DFW Rework
Rework A comes off the fourth MCA contact.
Rework B comes off the solder pad marked with a V.
Rework C comes off the third pin on the upper left of U23.
Rework D comes off the second pin of U23.
Trace cuts may have been made in addition to the rework wires.
Enhanced Differential SCSI Fast/Wide Adapter
FRU P/N 52G3380 (workee) (RS/6000 4-C)
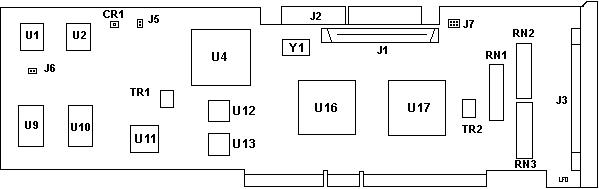
CR1 LED
J1 FW SE SCSI connector
J2 50-pin SE SCSI connector
J3 C68 DFW SCSI connector
J5 Leave open. Not used.
J6 Boot Enable
J7 2x3-pin diagnostic header
RN1-3 RS6K only?
TR1 PTC resistor for internal bus
TR2 PTC resistor for external bus
U1 SCSI microcode 88G1094
|
U2 SCSI microcode 88G1095
U4 82G2645 Int. SE SCSI ctrl. "Cutlass"
U5,18 NS DS36954
U9,10 CXK581000AM-70LL 128Kx8 SRAM
U11 AMD AM186EM-40VC MCU
U12 PAL 88G1092
U13 PAL 88G1093
U16 61G2323 MCA Bus iface "Malibu"
U17 52G9707 Ext. Diff SCSI ctrl. "Cutlass?"
Y1 40.0000 MHz osc
|
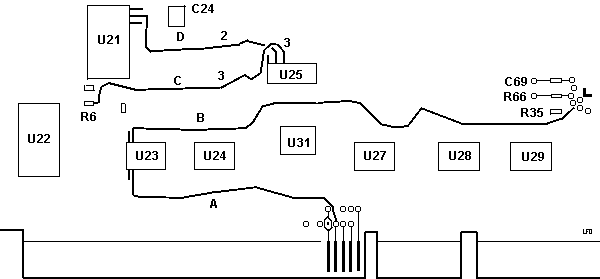
Rear of Enhanced DFW
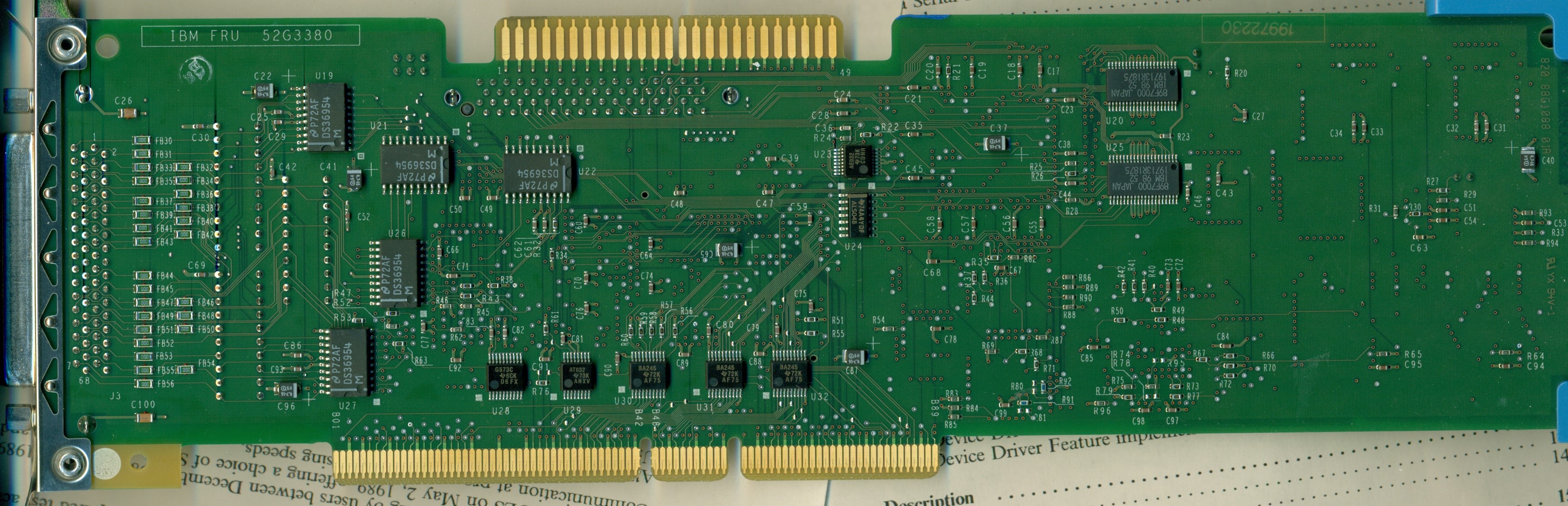
U19,21,22,26,27 DS36954
|
U20,25 89F7000 Term Network, SE
|
DS36954
Quad Differential Bus Transceiver
AN-904
Application Note 904 An Introduction to the Differential SCSI Interface
Why Five DS36954?
Remember, this adapter was used by AIX, and supports a high-reliability
configuration
"Five devices can implement a complete SCSI initiator or target interface.
Three transceivers in a package are pinned out for data bus connections. The
fourth transceiver, with the flexibility provided by its individual enables,
can serve as a control bus transceiver."
If you look at the further two DS36954 on the front (by the yellow
termpacks), it seems we would need five complete DS36594 plus one gate from a
sixth DS36594 for 16 bit SCSI, and the rest of the gates (three from the sixth
and four from the seventh) are used for control.
89F7000 Term Network, SE
These are the same parts used on the Corvette for
automatic termination of the internal Single Ended ports.
Jumpers on Differential Fast/Wide
The results of shorting the jumpers ranged
from no difference, slight performance hit (10% overhead
increase) or a system-halting error. Leave them off.
RS/6000 documentation says the jumpers are to be left
open.
J5 Grounds out pin 33 on the internal SCSI
controller 82G2645. Purpose unknown.
J6 Grounds out pin 1 of U1 and U2. Marked
"Boot Block Enable"
Corvette Turbo Capabilities
The SCSI-2 Differential Fast/Wide Adapter/A is a dual-ported, fast and wide
(two bytes wide) SCSI Micro Channel adapter that provides synchronous SCSI bus
data rates of up to 20MBps. The internal SE port is capable of addressing up to
seven SE SCSI devices and the differential external port is capable of
addressing up to seven differential SCSI devices, providing a maximum of 14
devices per adapter. The number of physical devices attached to each port is
limited by SCSI bus cabling restrictions. The external differential port can
support a total cable length of 25 meters (82 feet).
Additional system, subsystem and high-availability connections are also
available with the differential system-to-system and Y-cable features.
Corvette vs. Enhanced Corvette Turbo (from William R. Walsh)
Quick testing in the Server 95A upgraded to P180MMX shows a bit of a speed
improvement over the standard issue Corvette. Using a Seagate 10,000 RPM SCA
hard disk and UZ's "no-LED" driver, I got:
| Metric | Corvette
(single-ended) | Enhanced
Corvette Turbo |
|---|
| Max. | 11.5 MB/s | 13.7 MB/s |
| Min. | 10.6 MB/s | 13.0 MB/s |
| Avg. | 11.1 MB/s | 13.9 MB/s |
The Enhanced Corvette Turbo shows a CPU utilization of 10.4% compared to the
Corvette's 10.1%. Tests were run using the Simpli Software HDTach tool, which
was used before during SPOCK-206 NT driver testing.
Further Info
The differential F/W adapter is based on the same general architecture as
the single-ended variant.
See the SCSI F/W page for additional information
that applies to both adapters.
|