|
@8F97.ADF IBM SSA RAID Adapter
195-236 IBM SSA 4-Port Adapter for RISC System/6000
195-298 IBM SSA 4-Port Adapter Enhancements and Related Features for RISC System/6000
SA33-3270-02 Micro Channel SSA RAID Adapters Technical Reference (PDF)
SA33-3272-02 SSA Adapters User’s Guide and Maintenance Information (PDF)
SC23-1782-00 IBM Enhanced SSA 4-Port Adapter User's Guide and Reference (PDF)
SA33-3270-02 Micro Channel SSA RAID Adapters Technical Reference (BOO)
SA33-3272-02 SSA Adapters: User's Guide and Maintenance Information (BOO)
S31H-8612-01 SSA Adapters: Technical Reference (BOO)
SG24-5750-00 Understanding SSA Subsystems in Your Environment (BOO)
IBM SSA
Adapter Documentation Page (archived)
SSA Adapter Overview
SSA Port Header Pinout
SSA 9-Pin Mini-Ports
SSA Unitized Connector
Fibre-Optic Extender
PCI vs MCA Drivers
Note: This page describes the different IBM
pSeries SSA adapters.
SSA Adapter Overview
| FC |
ID |
FRU |
Name |
Bus |
Max / loop |
Name |
| 6214 |
4-D |
|
SSA Adapter |
MCA |
2 |
Mayflower |
| 6215 |
4-N |
|
SSA Enhanced RAID Adapter
Multi-Initiator RAID/EL Adapter |
PCI |
4 (R-5)
8 (R-0) |
Campbell 2 |
| 6216 |
4-G |
89H5667 |
SSA Enhanced Adapter |
MCA |
8 |
Mayflower 2 |
| 6217 |
4-I |
96H9883 |
SSA 4-Port RAID Adapter |
MCA |
1 |
Sarratoga |
| 6218 |
4-J |
|
SSA RAID Adapter |
PCI |
1 |
Beaulieu |
| 6219 |
4-M |
|
SSA Enhanced RAID Adapter ![Front [P]](/other/img/photo.gif)
Multi-Initiator RAID/EL Adapter |
MCA |
4 (R-5)
8 (R-0) |
Fremont |
| 6225 |
4-P |
|
Advanced SerialRAID Adapter |
PCI |
2 (R-5)
8 (R-0) |
Santa Cruz |
| 6230 |
4-P |
|
Advanced SerialRAID Plus Adapter |
PCI |
2 (R-5)
8 (R-0) |
Santa Cruz |
Note: All MCA adapters use devices.mca.8f97.*,
does this mean that they are all similar?
Notes: The 6215 and 6219 adapters appear to be
essentially identical other than the fact that the 6215 is PCI and the 6219 is
MCA (they both take the same microcode and appear to have identical
functionality).
Availability of TMSSA support may depend on what version of microcode is on
the adapter (the 6215 and 6219 adapters require at least level 1801).
The Advanced SerialRAID Adapters (6225 and 6230) are capable of 40 MB/sec
per direction per loop. The other adapters are capable of 20 MB/sec per
direction per loop.
Many of the values in the above table assume that the adapter has
sufficiently current microcode.
The Advanced
SerialRAID Plus Adapter Planning Guide states:
"The Advanced SerialRAID Plus Adapter has code above level 7600. The Advanced
SerialRAID Adapter had code below 7600 and that adapter can be converted to
support the additional functions by downloading code above level 7600."
i.e. the adapters are identical if they have sufficiently recent microcode.
This would seem to explain why the 6225 and the 6230 both are type 4-P.
J2, J6 - Internal SSA Connectors
The adapter card has 2 internal SSA connectors and 4 external connectors.
This allows one of the 2 dual-port SSA nodes to be connected either internally
or externally to the system unit. The internal connectors are 2 x 3 pin SSA
connectors.
Ports B1 and B2 have both internal and external connectors. The marking also
indicates that ports A1 and A2 are paired, that is, they are connected to the
same SSA loop interface chip. Similarly, ports B1 and B2 are paired.
+5 V power is available on the connector to power an external optical
extender.
SSA Port Header Pinout
Thanks to David Ress for finding this after I lost the reference... Pin 1 is
marked on the outside of the header on the PCB.
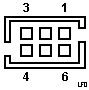
|
| Pin |
Signal |
Pin |
Signal |
| 1 |
Line Out+ |
6 |
Line Out- |
| 2 |
Ground |
5 |
Ground |
| 3 |
Line In- |
4 |
Line In+ |
|
J14 Exploration
Dave Ress tips back his miner's helmet and says:
I checked the SSA adapter I have, and it has the solder pads for a
6-pin port, but that is all. Looking at the A side and numbering the solder
pads from left to right, I find:
Pad 1 - GND
Pad 2 - Pin 5 of U7
Pad 3 - Pin 4 of U7
Pad 4 - Pin 3 of U7
Pad 5 - Pin 6 of U7
Pad 6 - +5 V
Looking at the SCC2691AC1A28
datasheet and
application note we learn that U7
is a UART, so the PS/2 port is really a serial port as the pins of U7 are
mapped as:
Pin 3 - RxD
Pin 4 - TxD
Pin 5 - MPO => multi-purpose output (clock pulse?)
Pin 6 - MPI => multi-purpose input (clock pulse?)
Beyond that, I have no idea where the U7 chip interfaces to. I tried to map
D0-7, but no luck there.
SSA 9-Pin Mini-Ports
SSA connectors are 9-pin high-density shielded ITT-Canon Micro MDSM
connectors.
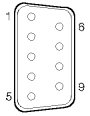
|
| Pin |
Signal |
Pin |
Signal |
| 1 |
Ground |
6 |
Line Out+ |
| 2 |
Line Out- |
7 |
Reserved/NC |
| 3 |
Ground |
8 |
+5 V |
| 4 |
Line In- |
9 |
Line In+ |
| 5 |
Ground |
|
|
|
The serial ports conform to SSA, Level 1. Each port operates at 20MB/sec
full duplex, using point-to-point copper cables up to 25 meters long.
SSA Drive Connectors
David Ress started diddling and said:
I took one of my SSA drives carriers apart this morning. It
originally went into a 7133.
I did this for two reasons: first, I have always wondered how to connect an
internal SSA drive up to the B1 and B2 internal connectors. Second, if the SSA
adapter has just a six pin ribbon connector, I was curious what the physical
connector looked like on the SSA drive.
In looking at the SSA drive carrier, the first thought was "what in the
world?", as the SSA drive carrier has a EURO 72-Pin style connector (think
mini-Nubus). 72-pin connector to support a 6 pin ribbon connector? But, as it
turns out, 32 of the pins are no-connect.
Further disassembling the SSA drive carrier revealed a IBM DFHC 4.5GB drive,
made in 1996. Note: the SSA drive carrier has a label that says assembled on 23
Feb 2000, I guess IBM had many units left over.
In removing the DFHC I learned that the connector is very unusual, unlike
anything I have seen before. I guess I was hoping to see a SCSI-2 connector as
SSA is a superset of the SCSI-2 protocol, but that was very much wishful
thinking on my part.
SSA Unitized Connector
SSA Unitized Connector
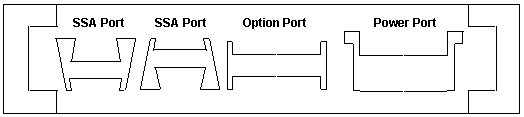
SSA Port on Unitized Connector
Option Port on Unitized Connector
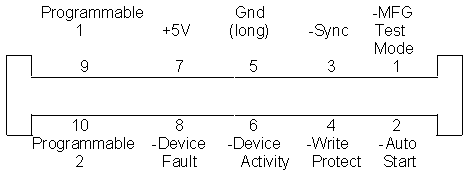
Power Port on Unitized Connector
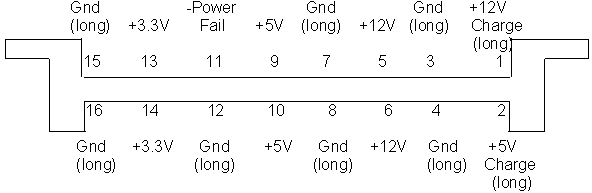
Carrier Connector
4x32 female contact, BERG HPC connector, part number 99F9429.
Ed. There seems to be different models with
different carrier interfaces (at least for the 4-G adapter). YMMV.
Fibre-Optic Extender
A fibre-optic extender is available to connect an industry-standard fiber
optic cable within an SSA loop when that loop is used with a 7133 SSA Disk
Subsystem. With a fibre-optic extender attached at each node, the distance
between them can be up to 2.4 km. The maximum sustainable data-transfer rate in
a single direction on an SSA link is approximately 18 MB/s. Extending the link
with a fiber optic cable results in no degradation of this data-transfer rate
for lengths up to 200 meters, and a gradual reduction in the achievable
data-transfer rate beyond this distance. This data-transfer rate reduction
generally has no effect on SSA subsystem performance for most applications.
PCI vs MCA Drivers
> Dave, are the PCI and MCA variants of the SSA adapter close enough for the
PCI drivers to work?
From my experiences in developing various drivers for MCA adapters under NT,
I will answer "no." This is due to the different way drivers scan their
expansion buses for adapters. PCI drivers scan completely different from the
way MCA drivers do. Some drivers, like the one I am working on with Ryan A.,
are written smart enough to scan multiple buses (in this case, it scans ISA,
EISA, MCA, and PCI), but I have found that to be extremely rare.
|