|
@8F62.ADF IBM 10/100 Mbps TX MCA Ethernet Adapter
Custom ADF created by Ryan Alswede based on AIX POS data and testing.
pcnet.tar 10/100 Mbps Ethernet Tx MCA Adapter AIX Disks (zipped disk images) [New!]
10/100 Mbps Ethernet Tx MCA Adapter Device Driver for RS/6000 (93H8201)
10/100 Mbps Ethernet Tx MCA Adapter (8F62) Device Driver & Diagnostics for RS/6000 (93H8197)
sanremo-win9x.zip Windows 9x Driver (by Christian Holzapfel & Ryan Alswede)
sanremo-winNT40.zip Windows NT4.0 Driver (by Ryan Alswede) [New!]
sanremo-linux-2.2.17.zip Linux Driver - source, kernel 2.2.17 patch & ADF (by Christian Holzapfel)
sanremo-linux-2.4.18.zip Linux Driver - source, kernel 2.4 patch & ADF (by Christian Holzapfel) [New!]
sanremo-linux-main.zip zipped Linux Driver repo (21 Nov 2023; original HERE)
197-075 RS/6000 MCA Systems Expand Communications Features;
Supplement (dead)
197-277 Enhancements for 10/100 Mbps Ethernet MC Adapter;
Supplement (dead)
10/100 Base Card
Daughter Card
9-K vs 9-Q
Defective 10/100 Ethernet MCA Cards
Card Resources
Technical Details
ASIC-9060R I/O Window Registers
ASIC-9060R Initialization
I/O Tunneling to the PCnet
Interrupt Handling
DMA Transfers
Accessing VPD Area
Linux Driver Performance
10/100 Mbps Ethernet MC Adapter
FRU P/N 07L6601 (FC 2964)
Base Card
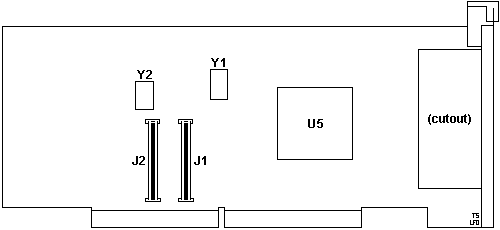
J1,2 64-pin mini-C64 female
U5 Adaptec ASIC-9060R PCI/MCA bridge
|
Y1 40.0000 MHz osc
Y2 32.0000 MHz osc
|
U5 Adaptec ASIC-9060R PCI/MCA bridge -
this is the only component that can be directly addressed from the host system.
The PCnet is a PCI busmastering chipset, so the ASIC is needed in order to
transform bus accesses through the card's MCA interface to the PCnet.
There is a big cut out in the PCB at the bracket end.
Chip date stamps are '97.
Daughter Card P/N 93H3236
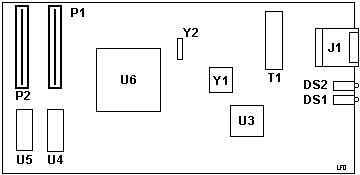
DS1 RCV/FDX LEDs
DS2 100/LNK LEDs
J1 RJ-45 connector
P1,2 64-pin mini-C64 male
T1 Pulse PE-68515
|
U3 ICS 1890Y PHY (brief)
U4,5 Alliance AS7C256-15JC
U6 AMD AM79C971KC PCnet-Fast
Y1 25.000 MHz osc
Y2 R200H85JT xtal
|
Interrupt levels 10, 11, 12, 15
Busmaster 80 MB/sec data streaming
Max 1, 2 or 4 depending on the model number
9-K vs 9-Q
There are two versions of this adapter:
- 9-K - FC 2964 - UNI version
- 9-Q - FC 2994 - SMP version
Physically FC #2994 and FC #2964 are identical. FC #2964 should only be used
on the UNI machines, FC #2994 can be used on either type of machine. The
electrical difference has to do with the I/O bus hogging issues and
performance.
Increased maximum number of adapters allowed on SMP systems.
Defective 10/100 Ethernet MCA Cards (ECA265)
The MCA socket edgecard is NOT beveled on a few 9-K and 9-Q adapters. They
can collapse the spring contacts inside the MCA socket on the planar. You can
(sometimes) pry the spring contacts back into alignment (I know, I had to do it
on my 7012-397).
Feature FRU ASM SYSTEMS
FC2994 P/N 07L6601 P/N 93H7888 7012-Gxx, 7013-Jxx, 7015-RXX
FC2964 P/N 07L6605 P/N 93H8060 7006-4xx, 7009-Cxx, 7012-39X
7013-59x, 7015-99x, 7030-3XT
This adapter can cause permanent damage to the I/O planar when it is being
installed or reseated. The slot pins on the I/O planar can become bent as the
adapter is plugged into the slot.
Important: This adapter should not be reseated, or
reinstalled in any slot once the adapter has been removed from the system for
ANY reason until the adapter has been reworked. The typical failure symptom is
"failure to configure".
Also inspect the I/O Planar slot for bent pins before installing the new
adapter. If pins are bent, replace the I/O planar at the same time you are
replacing the Ethernet card.
Some of the adapters have been reworked to correct the problem, others have
not. To determine if the adapter has the problem, inspect the adapter in the
tab area close to the I/O connector. The defective adapters will have a bottom
edge of the chamfer along the tab that is blunt instead of beveled, (the edge
of the chamfer will be flat rather than "V" shaped). See FIG. 1.
Bad:
FIG. 1
___________________________________________________________
| |
| |
| |
| 10/100 ETHERNET MCA CARD |
| |
| |
|______ ___ __________________________|
| | | | ____
| | | | | |
large-> \_______/ \_________/ | | <---adapter
chamfer |__|
_ _
I/O slot----> | | | |
| | | | end
| \__/ |<-view
|________|
Good:
___________________________________________________________
| |
| |
| |
| 10/100 ETHERNET MCA CARD |
| |
| |
|______ ___ __________________________|
| | | | ____
| | | | | |
round->'---------' '-----------' | | <---adapter
corner | |
_ \/ _
I/O slot----> | | | |
| | | | end
| \__/ |<-view
|________|
Physical Check
In addition, before removing the adapter you should inspect the metal end
plate for a blue dot which indicates that the card has been reworked and should
not be replaced. (see FIG. 2.)
FIG. 2. (end view)
_______
| |
| |
| O |<------blue dot
| |
| |
| |
| |
| _ |
| | | |<------RJ-45 connector
| '-' |
| _ |
|_| |_|
Card Resources
You can choose from the following resources:
- I/O address: 0x1C00..1FFF / 0x2000..23FF / 0x2400..27FF / 0x2800..2BFF
- IRQ: 10 / 11 / 12 / 15
- DMA arb level: 3 / 4 / 5 / 6 / 7
Technical Details
The information presented below was obtained via reverse engineering by
Christian Holzapfel (original HERE).
ASIC-9060R I/O Window Registers
The ASIC opens up a space of 0x400 bytes in the system's I/O port range, of
which only 0x30 bytes are actually used, while the rest is repetitions of the
initial 0x30 wide area. I call this the "ASIC I/O space registers", because the
ASIC places some internal registers here. The following ASIC registers were
identified (addresses are relative to the base I/O address):
Address
(ioaddr+) | Size
[B] | Access
(R/W) | Use | Value | Notes |
|---|
| 0x00 | 2 | WO | Init | 0x0006 | Written to on Init only |
| 0x02 | 2 | RW | ISR | 0x0000 | ASIC interrupt flags |
| 0x04 | 1 | WO | I/O Tunnel | 0x01 | Daughter card PCI config space access register |
| 0x05 | 1 | — | — | — | <unused> |
| 0x06 | 2 | — | — | — | <unused> |
| 0x08 | 4 | RW | I/O Tunnel | | Daughter card I/O address register |
| 0x0C | 4 | RW | I/O Tunnel | | Daughter card I/O data register |
| 0x10 | 4 | WO | Init | 0x00000000 | Written to on Init only |
| 0x14 | 4 | WO | Init | 0x00000000 | Written to on Init only |
| 0x18 | 2 | RW | ISR | 0x8008 | ASIC interrupt flags |
| 0x1A | 2 | WO | Init/ISR | 0x0FFF | Written to on Init (0x0FFF) and every ISR exit |
| 0x1C | 1 | WO | Interrupt | | Daughter card IRQ enable register |
| 0x1D | 1 | WO | Init | 0x00 | Written to on Init only |
| 0x1E | 1 | WO | Init | 0x4F | Written to on Init only |
| 0x1F | 1 | WO | Init | 0x04 | Written to on Init only |
| 0x20 | 2 | WO | Init | 0x03FF | Written to on Init only |
| 0x22 | 1 | WO | Init | 0x7F | Written to on Init only |
| 0x23 | 1 | — | — | — | <unused> |
| 0x24 | 1 | WO | VPD | 0x00 .. 0xFF | VPD index register |
| 0x25 | 1 | RO | VPD | Var | VPD data register |
| 0x26 | 1 | RO | VPD | 0x01 | VPD state/valid Register? |
| 0x27 | 1 | — | — | — | <unused> |
| 0x28 | 4 | WO | Init | 0x00000000 | Written to on Init only |
| 0x2C | 4 | — | — | — | <unused> |
ASIC-9060R Initialization
After setting up the POS registers by using the ADF, the card needs a few
accesses through the I/O window to initialize. The purpose of those accesses is
still unclear, but replaying the noted values seems enough to set the card in
operation:
outb(0x00, ioaddr + 0x1D);
outb(0x4F, ioaddr + 0x1E);
outb(0x04, ioaddr + 0x1F);
outl(0x00000000, ioaddr + 0x28);
outw(0x0006, ioaddr + 0x00);
outl(0x00000000, ioaddr + 0x10);
outl(0x00000000, ioaddr + 0x14);
outw(0x0FFF, ioaddr + 0x1A);
outb(0x7F, ioaddr + 0x22);
outw(0x03FF, ioaddr + 0x20);
outb(0x00, ioaddr + 0x1D);
outb(0x4F, ioaddr + 0x1E);
outb(0x04, ioaddr + 0x1F);
outl(0x00000000, ioaddr + 0x28);
outw(0x0006, ioaddr + 0x00);
outl(0x00000000, ioaddr + 0x10);
outl(0x00000000, ioaddr + 0x14);
outw(0x0FFF, ioaddr + 0x1A);
outb(0x7F, ioaddr + 0x22);
outw(0x03FF, ioaddr + 0x20);
I will not go into details of all the initialization sequences, as you can
find them inside the source code, hopefully commented sufficiently.
I/O Tunneling to the PCnet
Generally, the PCnet is able to work in two different addressing modes: WIO
(16-bit) and DWIO (32-bit). On the San Remo card, it is forced to work in "DWIO
addressing mode" only, and this seems to be the only mode the ASIC supports
tunneling. Usually the PCnet starts up in WIO mode and is shifted up to DWIO by
the driver; in this case, the PCnet initializes itself from the onboard EEPROM
which contains initialization data that sets it into DWIO mode immediately. If
you want to talk to the PCnet from your driver, you can't just read and write
to the card's I/O space directly, because you have to get past the ASIC. On the
PCI side of the ASIC (the PCnet side), the PCnet chip has an I/O window too, at
0x1000 offset. So if your card's I/O base address sits at 0x1C00, the
internal PCnet I/O base is 0x2C00, and so on. Tunneling works like
this:
- You have to write to the ASIC's Daughter card I/O address register at iobase + 0x08 the address of
the PCnet you would like to access, e.g. the RAP register at offset 0x14 inside the PCnet's range.
-> Write 0x2C14 to 0x1C08
- Then write to or read from the ASIC's Daughter card I/O data register at iobase + 0x0C:
-> Read/write from/to 0x1C0C
So for each usually single port access to the PCnet, in our case we have to do two, to get through the ASIC.
Accessing PCI Configuration Space
If you issue writing a '1' to the Daughter card PCI config space access
register at iobase + 0x04, the PCnet's PCI Config Space is available for 32-bit
wide access through the standard I/O tunnel registers iobase + 0x08 and iobase
+ 0x0C for exactly one immediately following access. The PCI Config Space can
be read and written this way.
Interrupt Handling
On the San Remo card, we have a PCI bus between the ASIC and the PCnet, and
an MCA bus between our CPU and the ASIC. When the PCnet raises an interrupt,
the ASIC picks it up, sets a bit in one of its registers and raises an
interrupt on the MCA bus for the CPU to pick it up.
The ASIC's interrupts are enabled by setting the first bit in iobase + 0x1C.
Clearing this bit inhibits MCA interrupts, no matter what's pending on the PCI
side.
So in order to clear a pending interrupt, the driver's ISR would have to the
following actions:
- Read the ASIC's interrupt flags at iobase + 0x18 and iobase + 0x02
- Service the PCnet's needs
- Acknowledge the PCnet's pending interrupt flags
- Acknowledge the ASIC's pending interrupt flags by writing the read
values back to iobase + 0x18, iobase + 0x02 and 0x0FFF to 0x1A.
DMA Transfers
Usually, the PCnet is a supreme busmaster on it's PCI bus. The ASIC
gracefully picks up busmastering requests from the PCnet, and translates them
into Micro Channel DMA requests using the PREEMPT#, ARB/GNT# lines, along with
DMA slave arbitration. All DMA handling is invisible to the user or driver.
Reserving a DMA arb level in the Reference Disk configuration is just for
allocating the resource for the ASIC, and avoiding conflicts with other
installed cards.
Accessing VPD Area
In the AIX / RS/6000 world, each adapter must provide a storage area where
the so called VPD = Vital Product Data can be stored and altered. This is
supposed to hold information about the card, it's revisions, and optional space
about customer information about where the card is installed into, among other
things. This data is stored inside a 256 byte EEPROM type 24C02 next to the
ASIC. It may not prove important in PS/2 systems, but accessing that storage
space works like this:
- Write the byte index (0..255) to the VPD index register at iobase + 0x24
- Read the stored byte from the VPD data register at iobase + 0x25.
- You could try writing to it, if you dare.
- The VPD state/valid register at iobase + 0x26 probably holds a "valid" flag for the checksum.
Linux Driver Performance
The driver/adapter was benchmarked using netio (v1.11) against a Core2Duo
system running Ubuntu 22.04. Adapter in full-duplex, 100 mbit mode.
Measurements were taken on an IBM PC 750 PCI/MCA machine with Debian "Potato"
2.2 and various CPUs.
With the stock Pentium 133 CPU, the card achieved about 3,200 KB/s. With
an AMD K6-III 400 CPU, the card achieved over 7,500 KB/s.
The driver still seems to hit CPU saturation, but the results are still
impressive for an MCA system. This may change with future revisions of the
driver.
|