|
Multistation vs. IBM PC
Japanese Display System
Expansion Bus and External Interfaces
Self-test Functions
Content created by "Mr. Tahara" (mirror HERE
and HERE). Edited by Tomáš Slavotínek.
Multistation vs. IBM PC
The following table is a comparison between the two platforms at the time of
introduction.
|
Multistation |
IBM PC |
| CPU |
i8086 8 MHz |
i8088 4.77 MHz |
| Memory |
Min. 256 KB
Max. 512 KB |
Min. 16 KB
Max. 256 KB |
Floppy
Drive |
2DD 640 KB
1 - 3 Drives |
2D 360 KB
0 - 2 Drives |
Display
Adapter |
Japanese Display
Adapter |
Option
MDA or CGA |
Screen
Resolution |
1024 x 768 (24-dot)
720 x 512 (16-dot) |
720 x 350 (mono)
640 x 200 (color) |
| Parallel Port |
Built-in |
Option |
| Serial Port |
Option |
Option |
| OS |
Kanji DOS
(Japanese DOS) |
IBM PC DOS
CP/M-86
UCSD p-system |
It has been a few years since the IBM PC appeared and its capabilities have
improved. One notable aspect is its screen resolution that became high enough
to display 24-dot Kanji characters. It is well known that when IBM in the US
developed the next hi-res iteration of the VGA standard (XGA?), it adopted the
resolution of the Multistation. The 16-dot resolution was also adopted in the
JX's extended display mode.
Japanese Display System
The original Multistation models didn't have a Kanji font in the hardware
(in the base configuration), and instead loaded the font from software.
Machines with only one floppy drive and no hard drive, required the otherwise
optional Kanji font card because there wasn't enough space on the floppy to
store the font. Mid-era models replaced the font card by Kanji ROM. The late
models came standard with the font ROM installed.
Expansion Bus and External Interfaces
The Multistation has a unique expansion bus that is completely different
from the IBM PC and subsequent MCA. As a result, compatibility with the wide
variety of PC/XT/AT, PS/2 and PS/55 adapters is completely non-existent.
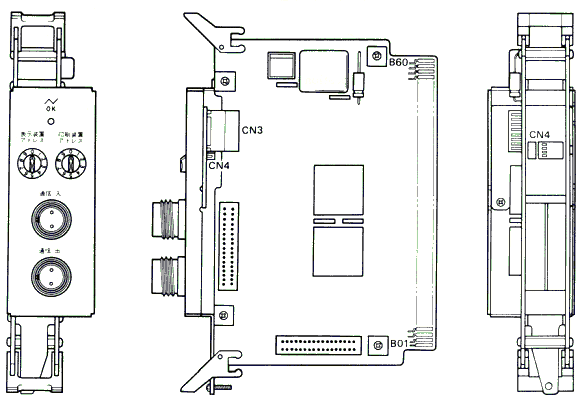
Example card - the 5250 Workstation Adapter (an older type that uses two slots)
The display and keyboard are also unique and not compatible with the other
computer families. The same is true for the parallel interface as it uses a
large 36-pin connector. The serial interface was originally sold separately and
was later built into later models.
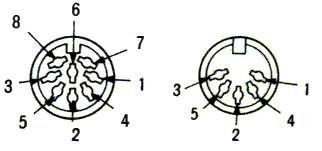
Left: Video output (monochrome), right: Keyboard
Self-test Functions
The Multistation has a self-diagnostic function built in, similar to the
POST and reference/diagnostic disc function of the MCA machines. There are two
types: the Basic Assurance Test (BAT) and the Resident Non-Automatic
Diagnostics (RNA).
Basic Assurance Test (BAT)
Similar to many other "modern" computers, the BAT is automatically executed
on power-on. When the power is turned on, the "IBM" logo and a counting up
number is displayed. When the diagnostic is completed, the operating system is
loaded.
The 5540 manual includes the following examples of error code meanings:
- One number only: There is a problem with the system unit
- 1xxx, 3xxx, Cxxx: There is a problem with the system unit
- A111: The keyboard cable is disconnected or there is a problem with the keyboard cable
- A112, A1D1: There is a problem with one of the devices
- Key symbol: The safety lock is locked or there is a problem with the system unit
- FFF2: The test switch is in the "Test" position
- F0xx: Memory error or insufficient memory
- Fxxx: There is a problem with the program being used or an abnormal interrupt occurred.
Resident Non-Automatic Diagnostics (RNA)
The RNA test was a diagnostic program that could be run from the
reference/diagnostic disk. It checked the system unit and expansion units for
abnormalities, and displayed error codes if any were found.
RNA starts only if the "Test switch" is in the "Test" position. When loaded,
a menu is displayed, allowing to test the entire system or only selected
components.
The following table was sourced from the 5540M/P manual.
| Test # |
Test Description |
| 0 |
If a dump diskette is placed in the drive, the memory contents will be written to it.
Option cards etc. can be tested if a system or diagnostic diskette is placed in Drive 1. |
| 1 |
Character attribute display (high brightness, reverse, blinking, etc.) |
| 2 |
Graphics mode display |
| 3 |
APA (All Point Addressable) test |
| 4 |
Diskette Drive 1 test |
| 5 |
Diskette Drive 2 test |
| 9 |
Test of the memory backed up by a lithium battery |
| 10 |
Printer wrap test |
| 11 |
Data printing test |
| 12 |
BAT start |
| 13 |
Memory test |
| 14 |
Font ROM test |
As you can see, some numbers are skipped.
"6" might have been "Diskette Drive 3 test" on models with 3 drives (5550).
Conversely, "14" might not be used on models without a standard font ROM.
|