|
@8FDB.ADF IBM XGA Display Adapter/A
C8FDB.ADF Init file for @8FDB.ADF
190-182 IBM PS/2 XGA Display Adapter/A
XGAUTIL.exe For use by P70/P75 display adapter.
XGAOPT.exe XGA/XGA2 Display Adapter Options Disk (details HERE)
xga212.exe XGA/XGA-2 Win3.1/ACAD/DQMS/DOS AI
XGA206 Windows 95/98 XGA-2 Display Driver by Unal Z
XGA208 Windows 9x and NT XGA/XGA-2 Display Drivers by UZnal
XGAKIT.ZIP IBM XGA Graphics routines. C and ASM Source. C Demo program.
VESA XGA Extensions Standard (VXE 1.0) (Thanks to Michal Necasek)
xgademo.zip XGA Demonstration v1.2 (easy install version by "Retro Erik")
(created by Mike O'Hara of Analyst International Corporation, 1992)
PS2 XGA Adapter Interface Technical Reference Sep 90
IBM VGA XGA Technical Reference Manual May 92
XGA: A New Graphics Standard by Jake Richter
The PC Graphics Handbook
Programming the XGA POS Registers
MSM514262 256Kx4 ZIP
MT42C4256Z-8 Datasheet
TN-42-01 Upgrading from 1 Meg to 2 Meg VRAMs
TN-42-02 Designing with MT42C4256/8128 VRAM
TN-42-03 Regular, Real-Time, Split Read Transfers
TN-42-04 Bank Interleaving w/ EDO VRAMs
TN-42-05 Four-Column vs Eight-Column Block Write
XGA Common Information
XGA Adapter
Adapter ROM
Win98SE Support for 64K colors
Linux Modelines
Invalid Aperture on NT
XGA Origins and Codename ("Expressway")
ADF Sections
XGA Adapter /A FRU P/N 75X5886, P/N 75X5887, FCC ID ANO75X5887
![Front [P]](/other/img/photo.gif)
![Back [P]](/other/img/photo.gif)
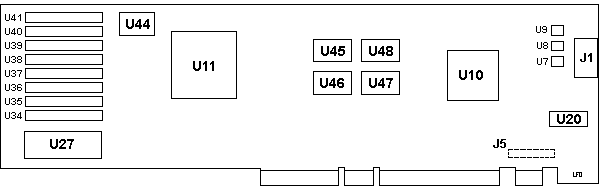
J1 HDD15 video connector
J5 Pads for 20-pin header
U7,8,9 TDK ZJY-2P
U10 37F0842 RAMDAC
U11 TC110GC9AG / TC110GC9AF
U2032Kx8 SRAM (sprite/attribute buffer)
U27 37F9567 video ROM
|
U34-41 Video RAM
U44 40.0000 MHz osc
U45 44.9000 MHz osc
U46 28.3220 MHz osc
U47 41.5390 MHz osc
U48 25.1750 MHz osc
|
U34-41 Toshiba TC524256BZ-10 or NEC D42274V-10
Note: -80 VRAM works fine!
TDK ZJY-2P 2 Line Common Mode Choke
datasheet
U10 37F0842 Serializer Palette DAC (INMOS IMS G190)
U11 TC110GC9AG XGA Display Controller (INMOS IMS G200)
U20 OKI M51257AL-12 or compatible 32Kx8 SRAM
(sprite/attribute buffer)
J5 Solder
pads for header to supply a base video. This function is
performed by the Base Video Extension (BVE) right below
the outline.
Oscillator Functions (from Peter)
U44 40.0000 MHz DMA Clock / 2
U45 44.9000 MHz Pixelclock 1024x768, 43.5Hz I (8514/A) mode
U46 28.3220 MHz VGA / Text mode
U47 41.5390 MHz Pixelclock 132-colums mode
U48 25.1750 MHz Pixelclock 640 x 480 / 400 modes
Different XGA Display Controllers
Early
TC110GC9AG / 1888676 9108
37F0842 19107 RAMDAC
Late
TC110GC9AF / 74F5160 9215 "BAKE"
37F0842 19323 RAMDAC
Model 90 Planar
TC110GC9AF / 74F5160 9214 "BAKE"
37F0842 19210 RAMDAC
I postulate that a new XGA Display Controller, TC110GC9AF / 74F5160 came out
in early 92. Note the Part Number for the original XGA Display Controller, IBM
P/N, 1888676... Sure reminds me of the Hursley designed Image Adapter/A...
Adapter ROM
1x 27C256-15 32Kx8 CMOS EPROM (U27)
(SGS Thompson M27C256B-15, AMD AM27C256-155, ST M27C56B-15FI, or compatible)
37F9576 XGA BIOS Ver 2.00 20-07-90
37F9576 XGA BIOS Ver ?.?? 15/03/91
XGA Block Diagram
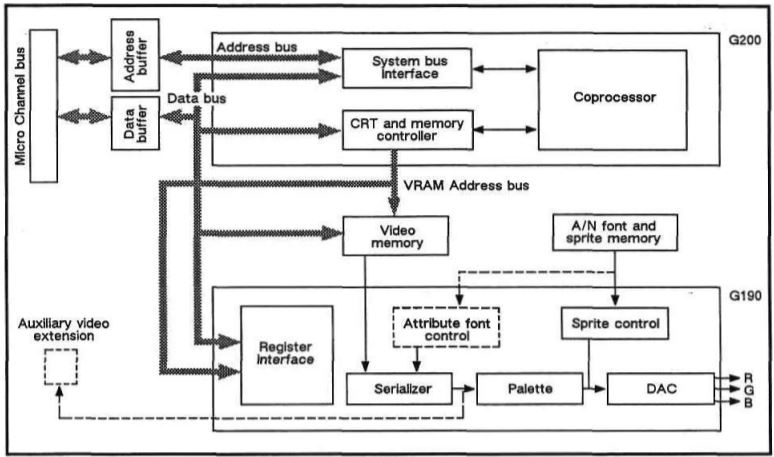
Flow of control and addressing signals, and the data flows from the external
interfaces (PS/2 interface and Base Video Extension) through the components to
the display.
XGA Adapter/A (standalone)
POST in Adapter PROM
Fits in Base Video Extension (BVE) slot, providing Base Video to AVE
(ex. Model 95)
XGA on planar
POST in the system ROM
Provides Base Video to Auxiliary Video Extension (AVE) (ex. Model 90)
XGA CPU Requirements
The XGA
Adapter/ A can be used in all Micro Channel machines with a 80386, 80386SX or
i486 processor. 80286 (and earlier) processors lack 32 bit registers and
segment registers.
XGA Slot Width
The XGA Adapter/ A
performs faster in a 32-bit slot, but it will still run in a 16-bit slot.
However, for 32-bit operations, it will require two bus cycles instead of one,
and memory addressability will be limited to 16MB.
XGA VRAM Size
Both planar and
Adapter/A perform faster with 1 MB because the data path into the video display
buffer memory is 32-bits wide. At 512 KB, the data path width is only 16-bits
wide.
W98SE Supports 64K Colors
Yes,
folks, I have been to the mountaintop, and it is good. W98SE has built-in
support for 640x480 at 16/256/64K colors (finally!) and 1,024x768 at 16/256
colors.
Linux Modelines (Xfree86 Beginning)
Chipset "XGA-1"
Instance 6 (Address from Video Instance)
IObase 0x2160 (Address from Video Instance)
COPbase 0xdff00
MEMbase 0xfd800000
BIOSabse 0xde000
DACspeed 45 (fixed)
Videoram 1024 (Easy, it's either 512 or 1024)
Clocks 28.322 25.175 41.539 44.9
XGA Generalities
The XGA card is a Base Video card - it does not need a planar video
subsystem. It is a Bus Master, able to do its own processing and memory
accesses without using the system processor, providing faster video processing
and freeing up the main CPU for other tasks.
The drivers and the card have been optimized to work with the 386 32-bit
instruction set. The max resolution with 512KB of VRAM is 1024 x 768 with 16
colors, with 1MB the max is 1024 x 768 with 256 colors. When upgraded with the
512K (PS/2 Video Memory Expansion Option), the XGA adds 640 x 480 with 65,536
colors in Direct Color Mode.
Invalid Aperture on NT
On IBM PS/2 computers with a 16-bit bus, and XGA, the following error
message may appear after installing the XGA drivers in Microsoft Windows
NT:
"The aperture enabled for the XGA device is invalid, please enable the 4MB
aperture (preferred) or 1MB aperture using the XGA reference disk."
This error occurs on 16 MB 16-bit bus PS/2 computers that support a maximum
of 16 MB of RAM, such as the model 9556 or 9557.
Cause
The PS/2 XGA subsystem provides three possible apertures, or windows, to
video memory in the physical memory address space of the system. Aperture size
options are 64KB, 1MB, and 4MB. The 4MB aperture option is not available on
16-bit computers, such as those based on the 80386 SX processor. The 4MB
Aperture is not available if the XGA subsystem is in a 16 bit slot in a 32 bit
computer and is only accessible by 32 bit protected mode drivers, such as the
drivers used by Microsoft Windows NT.
Currently, Microsoft Windows NT only supports XGA with an Aperture of 1MB,
or 4MB enabled. On 16-bit IBM PS/2 computers with 16MB RAM, the 1MB meg
aperture cannot be enabled.
Workaround
According to IBM, a possible workaround is to use the standard VGA which
does not require this option to work, or decrease the amount of physical RAM
below 16MB.
Installation Instructions
(source)
Installation of the XGA card is much like any other Micro Channel adapter.
First, simply place the card in a Micro Channel expansion slot. A 32-bit
slot is preferred, due to the speed advantage. There is however one slot the
XGA card will not fit, and that is the slot with the AVE. The XGA card does
have an extension that looks much like the 8514/A extension; however, upon
closer inspection you will see the extension on this card is positioned
differently. The positioning of the XGA extension tab will prevent it from
being inserted into the slot with the auxiliary video extension.
The XGA card only occupies 8KB of memory between 640KB and 1MB. Since the
XGA card is a Bus Master, it can occupy any 8KB in the "C" or "D" range. To see
which part of memory is being used by the XGA card, choose the menu option
"Display Memory Map" from the Reference Diskette. Another great feature of the
XGA card is that you can have up to six XGA cards installed in one machine
(five if the system has XGA already on the motherboard, like the Model 90). To
take advantage of multiple adapters, software must be specifically written to
do so.
If you have an XGA card in a system that has VGA on the system board and a
display attached just to the XGA card, the XGA card will function in VGA and
high resolution modes. Now, if you have the same setup as before but a display
is attached to the motherboard VGA port and another to the XGA card, all VGA
(and lower modes) will be displayed on the display attached to the motherboard
port. The XGA card will only be used when high resolution is required. You will
not get an echo of a VGA image onto the display attached to the XGA port as you
would using the 8514/A.
Once the card is installed, the appropriate device driver must be installed
before the high resolution can be accessed. There are two device driver
diskettes that come with the XGA card. The first diskette contains all of the
device drivers for DOS, Microsoft Windows 3.0, Microsoft Windows 286 2.1, and
AutoCAD Release 10. The second diskette contains support for OS/2 1.2 (OS/2 1.3
ships with an XGA driver).
XGA Origins and Codename ("Expressway")
Hardware
Products Developed at Hursley "Expressway" - XGA Adapter
Spacemont (a portmanteau of Space Mountain at Disney World being the highest
point in Florida) was a project between Hursley and Boca to develop a follow-on
to the VGA PC graphics adapter. However, it fell foul of compatibility and cost
issues and was canned after 6 months in favor of an extension of the VGA
(called rather unexcitingly the XGA).
The processor and pixel engine were the starting point for Image Adapter,
and the pixel engine was the starting point for the drawing engine of XGA. In
collaboration with IBM Research, Yorktown, the simulator created to test the
Spacemont VLSI before manufacture, General B, was also used effectively on
Image Adapter development.
1987 PS/2 Image Adapter/A Combined video display and (optional) printer
adapter supporting virtually all IBM PC monitors at the time, and a number of
3rd party image printers. Used CMOS-2 chip developed at Hursley (Cotswold
II).
AdapterId 8FDB XGA Display Adapter/A
Video I/O Address
I/O address range for display controller
registers. This also affects the location of video
coprocessor registers. Each XGA adapter must have a
unique address range.
<"Instance
6: 2160h - 216Fh">, 1 (2110-211F), 2
(2120-212F), 3 (2130 - 213F), 4 (2140- 214F), 5
(2150-215F), 7 (2170-217F), 0 (2100-210F)
1 MB VRAM Aperture Base
Address
1 MB aperture from PC into video memory. If
aperture has been disabled, it is because there wasn't
enough available memory address space for system memory
and the aperture.
Removal of system memory may degrade system
performance. If aperture has been allocated an
address range and it results in a reduction of usable
system memory (with Micro Channel memory adapter)
then the aperture can be disabled.
(Ed. On most systems
with >16MB, disable the aperture)
<"Address
at 15 MB (F00000h)" (0F000-0Ffff)>, 14 MB
(0E00-0Efff), 13 MB (0D000-0Dfff), 12 MB (0C000-0Cfff),
11 MB (0B000-0Bfff), 10 MB (0A000-0Afff), 9 MB
(9000-9ffff), 8 MB (8000-8fff), Disabled
Video Arbitration Level
Arbitration level the adapter uses to
transfer data.
<"Arbitration
level 13">, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 14, 7
Video Fairness
(Bus Arbitration) controls if adapter releases
control of bus after using it exclusively.
<"Fairness
On">, Fairness Off
ADPItem 1 ROM Address Range
8K block of memory assigned to
adapter. Only one XGA or XGA-2 Display Adapter
will have the ROM assigned, and any other XGA or XGA-2
Adapter installed will share that address range.
|